10cm Windfarm Cable Survey by GeoScope 100
2022-05-16
Products:GeoScope 100 Surface
Date:December, 2021
Location:Shengsi near Zhoushan
Dia.of the pipe: 10cm diameter 110KV windfarm cable
Speed of Veddel:4 knots
Installation: by the side
Wind farm cable diameter from 10cm-30cm specifications vary, 10cm diameter cable for the parametric array of shallow bottom profile detection technology is quite challenging, the following data really shows the actual detection of 10cm cable map. In these data, personal experience will lead to a certain bias in the judgement, we have some disagreement with the user on the judgement of the cable, the following as far as possible will state the basis of our judgement. In doing this very small cable diameter discrimination, the three most important things against the coordinates, against the coordinates and against the coordinates.

Data Display:
For the following data, we have circled as many targets as possible that we feel are suspect, if you feel they are not, then they are not, after all, no one has gone digging to find out. It is our philosophy of sharing to ensure the authenticity and complete presentation of the data. We don't need to go to the ball in our crystal shoes and embarrass ourselves after 12 o'clock.
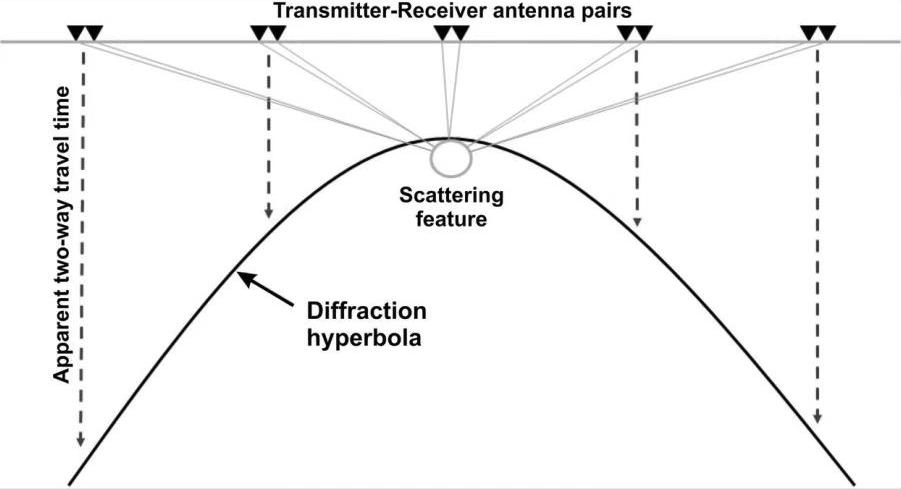
Fig. 1 Subbottom Profiler wraparound arc formation principle
The reflection formed by the sound wave hitting the cable is mainly reflected in the data in the form of a wrap-around arc, if you don't understand what a wrap-around arc is, you can look at this schematic diagram in Figure 1. That is, with the edge of the open corner of the first touching the target, the formation of the echo is to acoustic transmission time mark, so the formation of a hyperbolic-like arc around the shot.
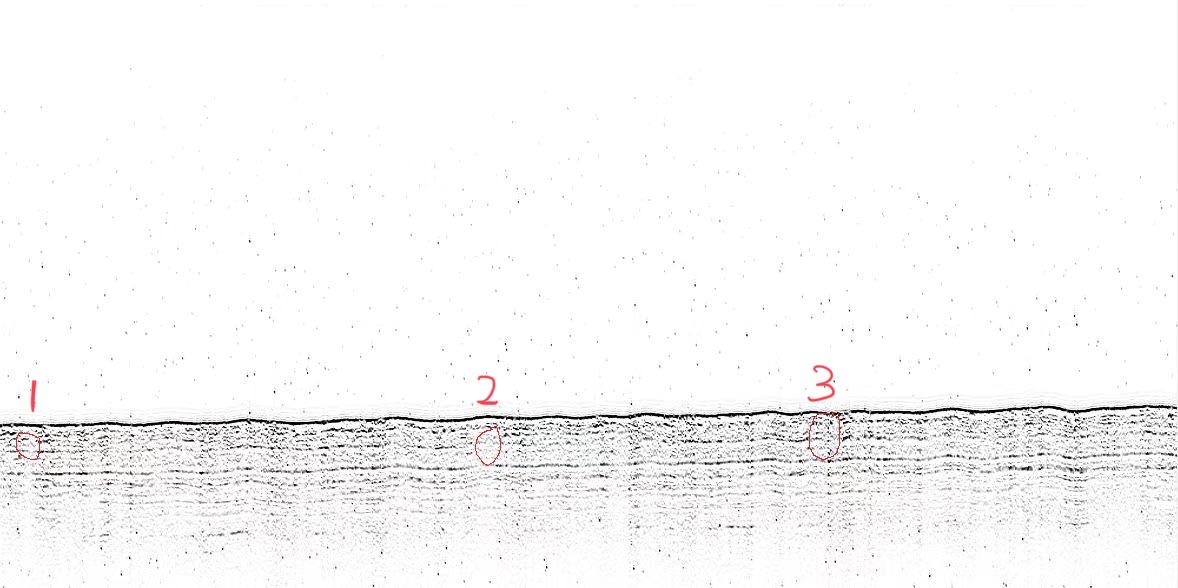
Fig.2 Three Suspected Cable Target
The presence of the cable can basically be determined by the combination of the arcs and the acoustic blanking underneath the cable due to the reduced energy. This is the most typical performance in cable detection, as shown in the 1st and 2nd marks in the above figure.
Of course, there is not always an acoustic blanking in every detection, but it is also possible that the phenomenon of multiple bypasses is formed under the factors of high ping rate, strong reflective stratum, and strong reflective cable material. This is shown in Figure 2, mark 3.
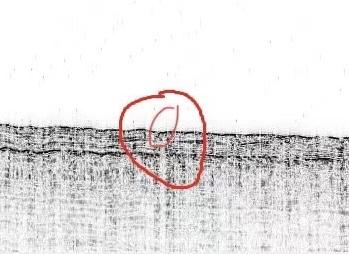
Fig.3 Arc and Acoustic Blanking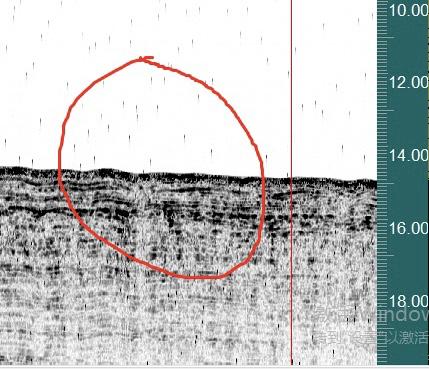
Fig.4 Arc and Acoustic Blanking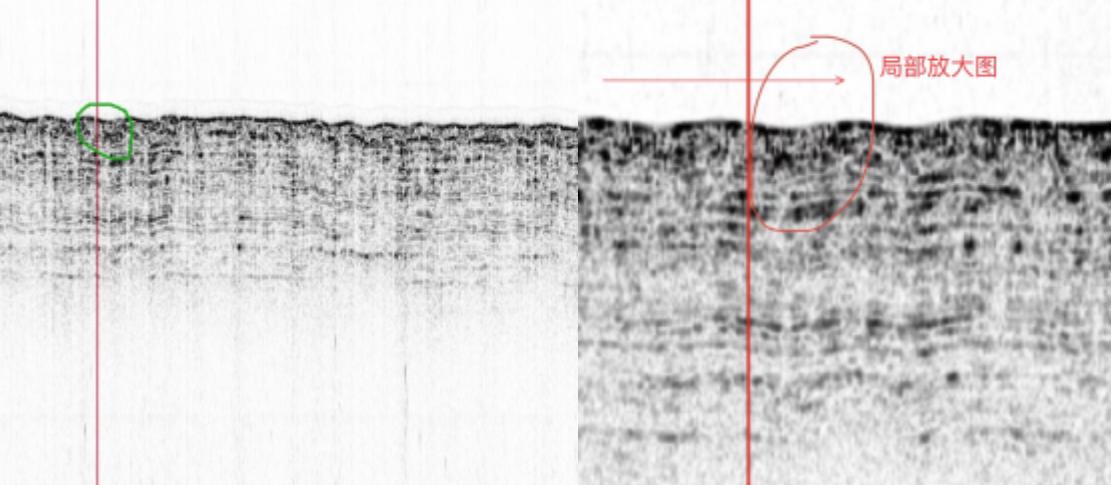
Fig.5 Arc and Acoustic Blanking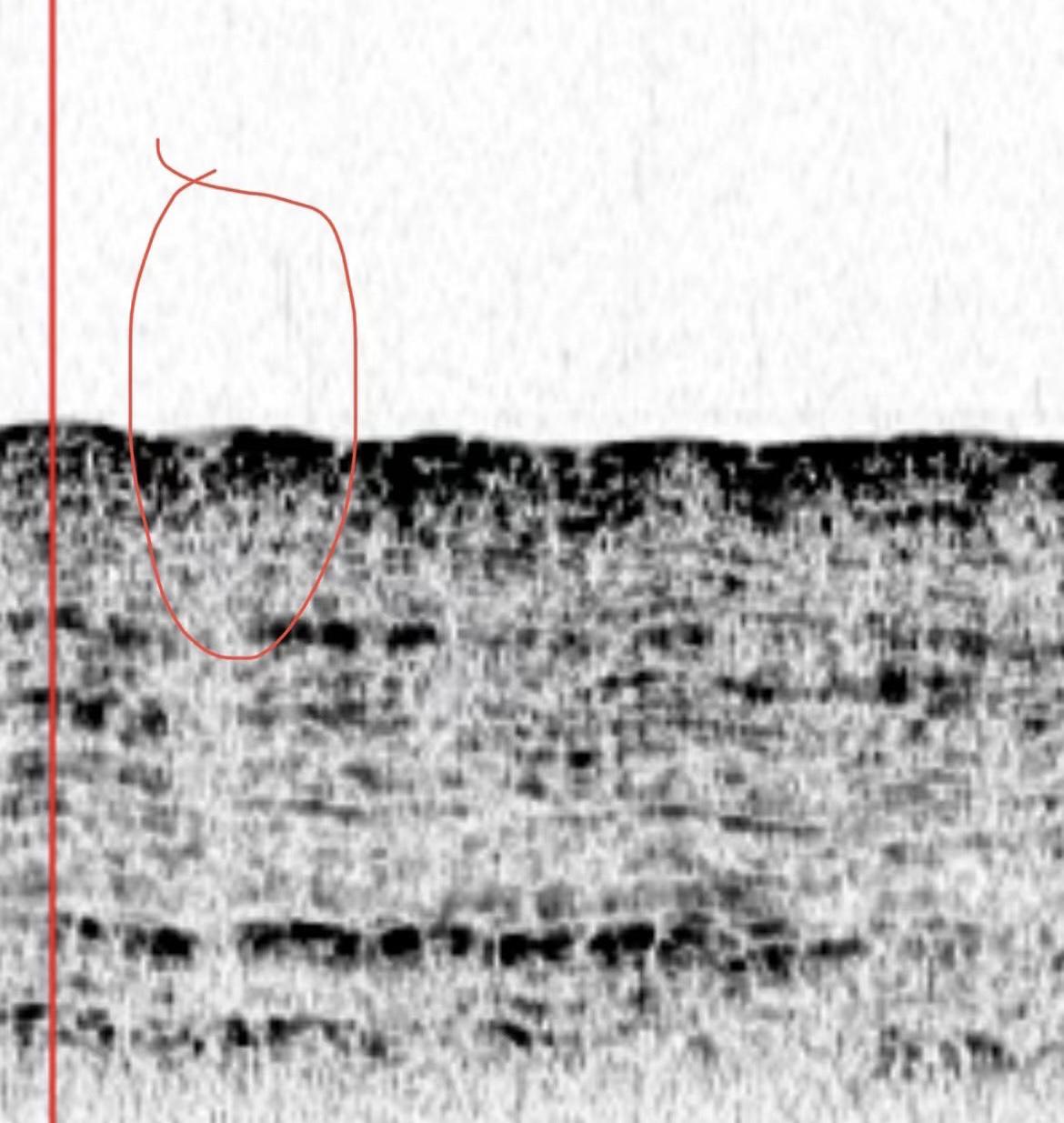
Fig. 6 Upper stratigraphic disturbance + Arc + Acoustic blanking
Figure 6 There is a disturbance in the stratum above the cable, which is suspected to be a gully dug during the burial of the cable, and the reflection of the medium in the gully is also different from the surrounding area, and the author deduces that it should be a cable that was constructed not long ago.
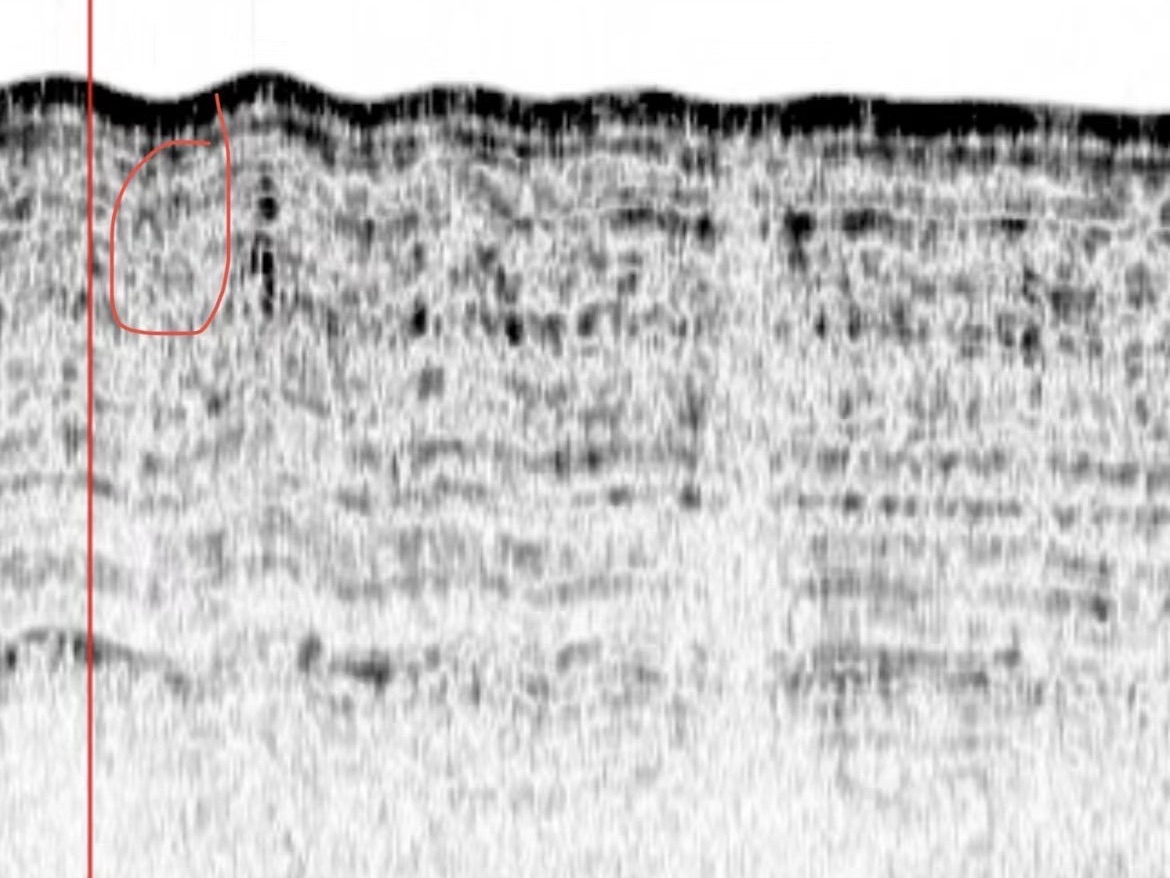
Fig.7 Arc
This type of arc is more pronounced, but there is no very significant energy loss underneath, which also exists and is usually also related to the material of the cable.
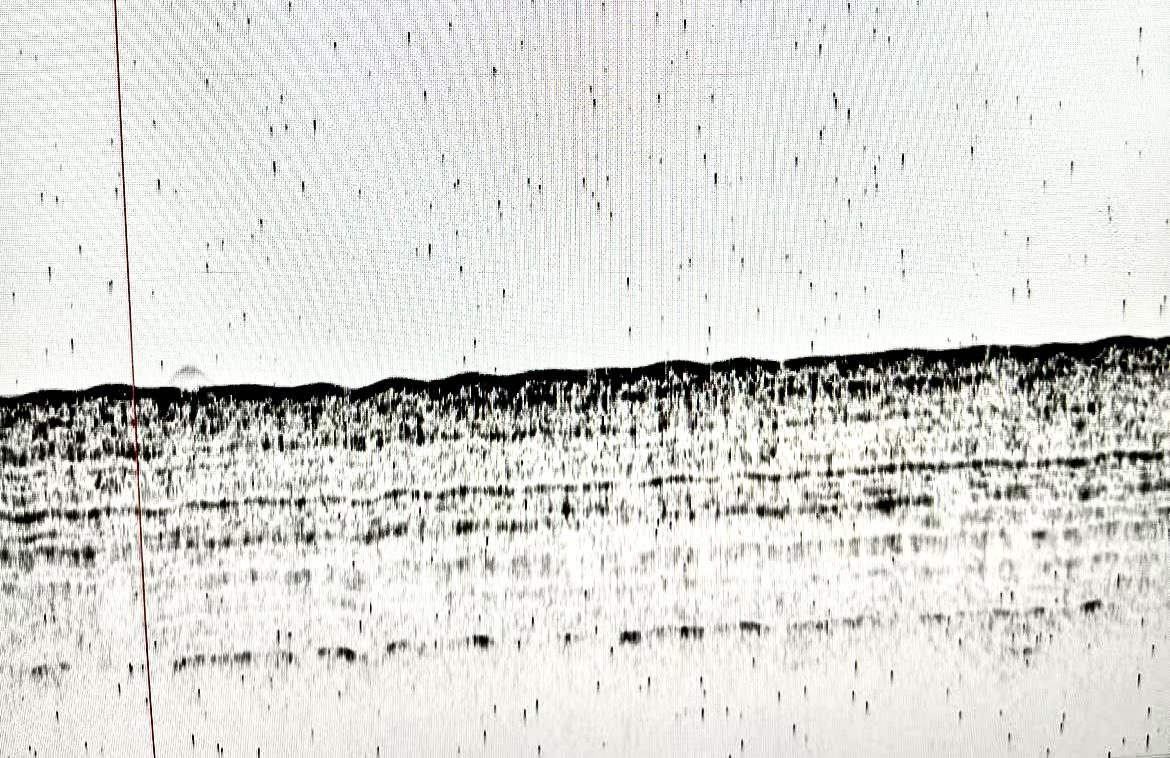
Fig. 8 Cables exposed on the seabed (approx. 12 cm diameter)

